Fusing Resistors
With miniaturization and enhanced functionality/performance of electronic equipment, the importance of circuit protection components to ensure the safety of electronic circuits is increasing.
Resistors normally function as resistors, but there are “resistors with fuse function” that have the function of interrupting the circuit current by activating the fuse in the event of an abnormality.
In this column, we will explain the fusing mechanism, usage precautions, and usage examples, especially for “fusing resistors” among various resistors.
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Ⅰ.What is a fusing resistor?
1.Classification
Resistors with fuse function include “fusing resistors” that use the fusing of resistance elements specified by JIS, and “thermal fuse incorporated resistors” that integrate a thermal fuse and a resistor. We have a lineup of products that correspond to both fusing resistors and thermal fuse incorporated resistors.
Figure1. Classification of fusing resistors
*List of Fusing Resistors https://www.akaneohm.com/prd_cat_use-eng/fuse/
JIS stipulates the meaning of fusing resistors as follows.
JIS C 5602-1986 2211 fusing resistor
A resistor that normally functions as a resistor, and when overcurrent that exceeds the specified value flows, the resistance element fuses within a specified time, blocking the flow of current and preventing the resistance value from returning to its original value. (fusing resistor)
This section provides an overview of fusing resistors and thermal fuse incorporated resistors.
1) Fusing resistors
A fusing resistor works as a fuse by using the fusing phenomenon of the resistive element formed in the insulator. Flame-retardant coating is used for the exterior of fusing resistor because the resistive element reaches high temperature. It normally functions as a resistor and is used in places where it should be fused safely in the event of an abnormality in the circuit. However, fusing resistors require a certain amount of time to fuse, and are generally slower to react than fuses. This should be considered when using fusing resistors.
Figure2. Structure of a fusing resistor
2) Thermal fuse incorporated resistors
The thermal fuse incorporated resistor has an integrated structure by incorporating the thermal fuse together with the resistive element.
There are also products that have acquired safety standard UL1419 certification, so they can be used as resistors for preventing inrush current in power supplies.
Figure3. Structure of a thermal fuse incorporated resisto
Ⅱ. Standards for fusing resistors
This section explains the standards for fuse function and resistance function based on the definition of terms for fusing resistors by JIS.
This section is about the standards for fusing resistors in more detail with reference to the definitions of fusing resistors by JIS described in the previous section.
Since various fusing resistor products are originally resistors, each series is standardized to satisfy the performance as a resistor.
Figure4. Resistor
Power rating and fusing time are specified for each series.
In the case of the fusing resistor FRN series, they are as shown in the figures below.
Figure5. Fusing Characteristics
When an overload is applied, the resistive element heats up, and finally fuses when the resistive film reaches the fusing point.
The “fusing” means the state that the resistance became a hundred times as larger than nominal resistance.
Figure 6. Fusing of a fuse resistor
As mentioned in the previous section, fusing resistors have a fuse function in addition to normal resistors, so the maximum working voltage, maximum overload voltage, and pulse resistance in particular decrease among the performance as a resistor.
The figures below show the comparison of the characteristics of the standard metal film resistor “RN series” and the fusing resistor “FRN series”.
Figure 7. Comparison of characteristics of standard resistors and fusing resistors
Figure 8. Pulse power limit
Please check the characteristics of each series carefully when considering using them.
→Please contact us if you have any inquiries.
Ⅲ. Fusing characteristics and fusing mechanism of fusing resistors
The following is about the fusing characteristics and fusing mechanism using the fusing resistor “FRN series” as an example.
The structure of our fusing resistors is the same as general resistors with lead wires.
However, since a material dedicated to the fuse function is used for the “No.4 Resistive film (fusing film)” in the Figure 9, it has specifications that facilitate the fusing mechanism shown below.
Figure9. Structure of a fusing resistor
The fusing process of the fusing resistor is as follows. (In case of constant voltage circuit)
①When an overload is applied, the resistance value changes to a lower value due to Joule heat(*).
② As the resistance decreases, the power consumption P increases according to the formula “power P = V2/R”, which increases the amount of heat generated.
③ When the amount of heat generated increases, the state of ① will be further accelerated, and the amount of heat generated will increase further due to ②, eventually leading to fusing state when the resistive film reaches the fusing point.
*The reason why the resistance value decreases is that the conductivity increases due to the change in the crystal structure of the resistive element.
The resistance value of the fusing resistor drops once in the process of fusing, and then it becomes open. It may drop to a maximum of -80% of the initial value, so depending on the circuit conditions, there may be cases where the current capacity is insufficient (constant current circuit) and the resistance value is kept in a state of decreasing or increasing without leading to fusing.
Please carefully check and verify fusing resistor products on the actual machines when using them.
Figure 10. Fusing characteristics of fusing resistors
Ⅳ.Precautions for using resistors with fuse function
The precautions for using resistors with fuse function are shown below.
Also, please carefully check and verify fusing resistor products on the actual machines when using them.
Ⅴ.Usage example of resistors with fuse function
1.LED current limiting resistor
In an LED circuit, a resistor connected in series with the LED suppresses the current below its rating.
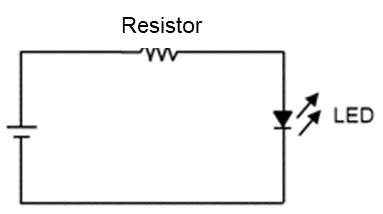
Figure 11. LED circuit
If the circuit described above goes into short-circuit mode due to factors such as LED failure, the main protection circuit may not work and the resistor may burn out depending on the supply voltage and resistance value. In such cases, it is recommended to use fusing resistors “FRN series” to prevent the resistor from glowing and igniting.
The MOSFET’s source resistance limits the primary-side current and is used as a current sensing resistor. If a large current flows due to a failure of the MOSFET, the resistor may emit smoke or ignite. In such cases, it is recommended to use fusing resistors “FRN/FWF series” to prevent the resistors from glowing and igniting.
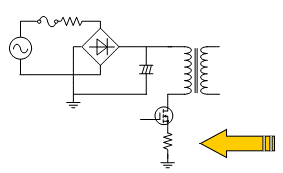
Figure 12. Power circuit
In the power supply circuit, since the smoothing capacitor is charged when the power is supplied, a large current may flow and cause malfunction of the device.
Therefore, current limiting resistors are used to prevent inrush current when the power is supplied. In such cases, resistors with fusing function are sometimes used for safety. We recommend the RWT05A series, thermal fuse incorporated cement resistors that have acquired UL and CSA certification.
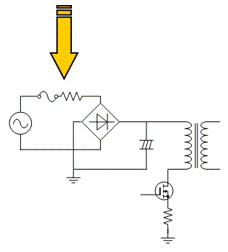
Figure 13. Power supply circuit
As toys are used by children, safety is a top priority for the circuits used in them.
Since toys are often used frequently, malfunctions that cause large currents may occur due to impacts during use. In such cases, we recommend using the CFD series, “over current limiting resistors” to prevent heat generation accidents due to large currents.

Figure 14. Circuit of toy
Ⅵ.Lineup of resistors with fuse function
UL and CSA certified products are also available. Our fusing resistors that are most suitable for ensuring the safety of electronic circuits are introduced below.
[1] Fusing resistors with lead wires
<FRN series> Fixed Fusing Resistors
https://www.akaneohm.com/products-data-eng/frn/
[2] Over current limiting resistors with lead wires
<CFD series> Over Current Limiting Resistors
https://www.akaneohm.com/products-data-eng/cfd/
[3] UL and CSA acquired resistors suitable for power supply circuits (primary and secondary)
<RWT05A series> Thermal Fuse Incorporated Cement Resistors
https://www.akaneohm.com/products-data-eng/rwt05a/
[4] Thermal fuse incorporated resistors
<RWT series> Thermal Fuse Incorporated Cement Resistors
https://www.akaneohm.com/products-data-eng/rwt/
[5] Cement type fusing resistors
<FWF series> Cement Type Wirewound Fusing Resistors
https://www.akaneohm.com/products-data-eng/fwf/
<NOTE> This document is subject to change without notice.
Please check the latest information when considering using our products.
→Please contact us if you have any inquiries.
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
→Click here to quickly search products by power rating & resistance value.
→Please contact us if you have any other inquiries.